 Search
Search
 Search
Search
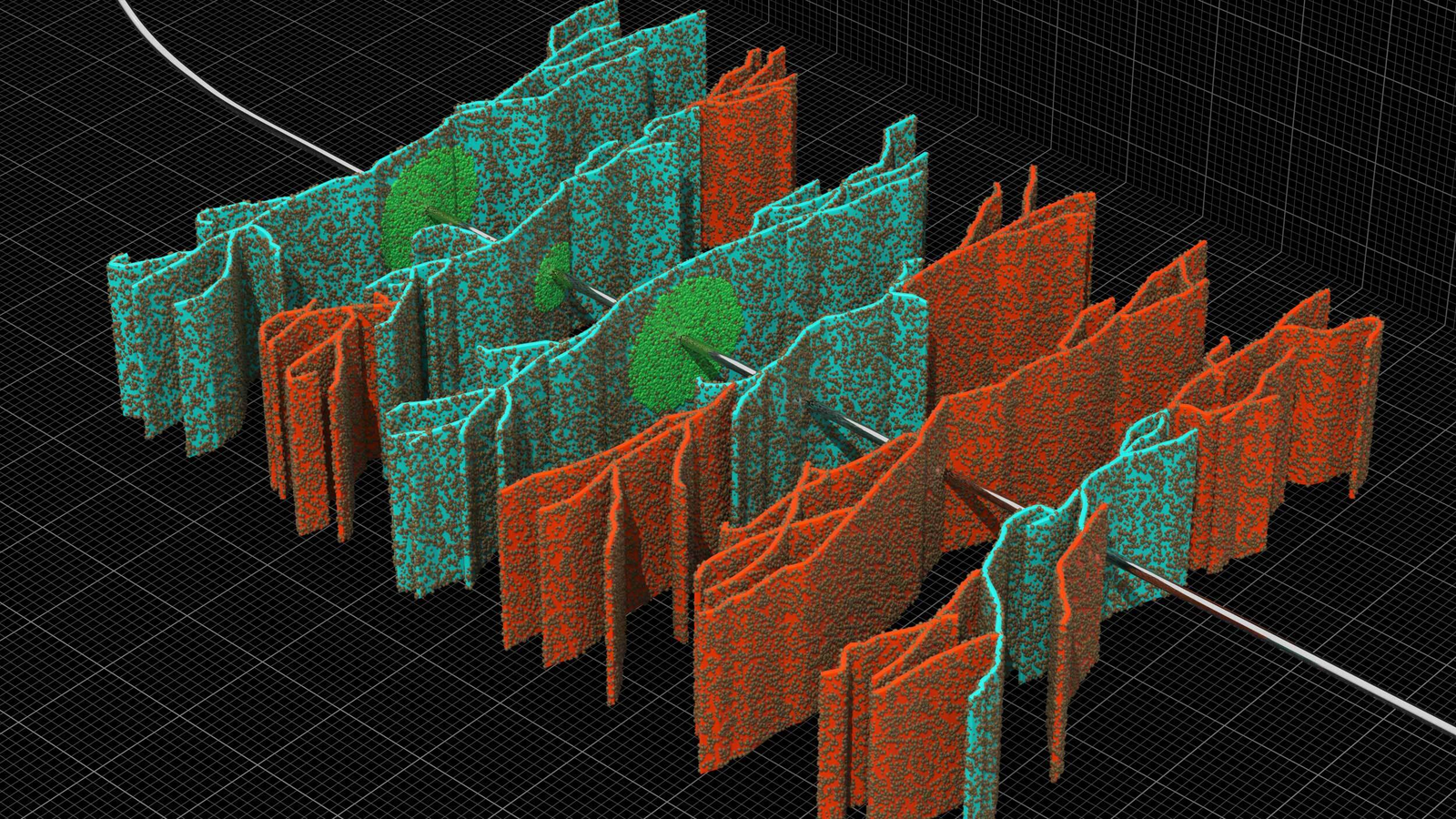
ChannelFix™ cement additive fills mud channels in high-pressure reservoir drilled with low-erodibility mud
Download PDFDeepwater
Provide zonal isolation in the pay zone with high pore pressure
West Arabian Gulf
In high-pressure/high-temperature (HP/HT) environments, low-erodibility mud can pose significant risk to the cement operation and potentially compromise well integrity. Because of its low mobility, it is resistant to displacement by cement. This can lead to incomplete mud removal and leave behind mud channels or filter cakes that prevent cement from bonding properly to the casing and formation. Conventional wellbore conditioning practices are often ineffective to fully remove low-mobility wellbore fluid.
An operator in the Middle East planned to drill wells in an HP/HT offshore environment to incorporate new reservoirs. Use of synthetic oil-based mud (SOBM) with a low erodibility profile risked the creation of mud channels through the cement. Given the narrow operative window between pore pressure and fracture gradient, it was crucial to establish effective displacement so that uncemented pathways, which can lead to fluid or gas migration, do not form.
Halliburton proposed a gas-tight slurry optimized with ChannelFix™ cement additive. ChannelFix additive swells through contact with oil-based mud (OBM) or synthetic-based mud (SBM), which helps fill mud channels and create a barrier capable to withstand more than 2,500 psi per 10 ft (3 m) of annular space to improve the zonal isolation across wash-out and low-erodibility zones.
The solution was tailored with iCem® cementing service 2D and 3D hydraulic modeling, which included erodibility analysis, 3D displacement efficiency, and predictive bond log analysis to help achieve the maximum displacement efficiency and radial cement coverage. Proper rheological hierarchy was maintained to help optimize removal of the low-mobility SOBM.
Coverage cement barrier achieved
Signs of mud channels
Remediation required
Validated zonal isolation
The operator achieved a full coverage cement barrier in the entire cemented interval with no signs of mud channels, which was validated by CBL/CAST bond log evaluation. No remedial operation was necessary, which allowed the well to move directly to the test and appraisal phase.
Due to this success, the operator chose ChannelFix additive as the preferred solution to address cement challenges in the pay zone, particularly where there is a high risk of mud-channel formation caused by washed-out intervals or low erodibility mud systems.
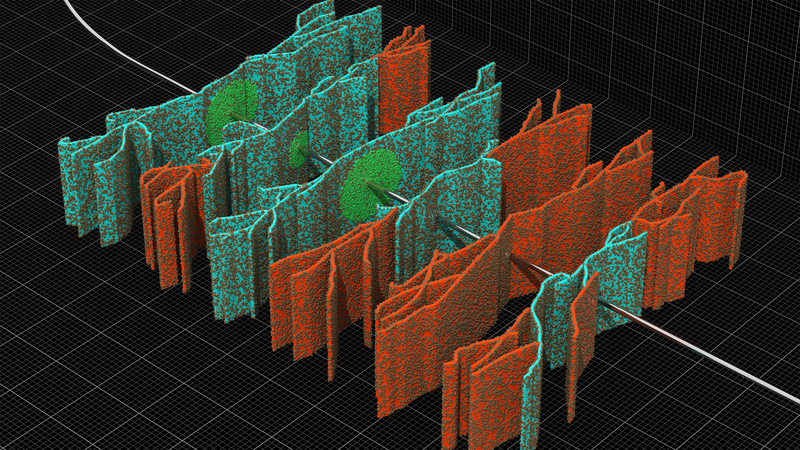
Swelling solution designed for barrier dependability and helps provide increased cement sheath elasticity.

Cementing barrier design and tailoring digital twin software that enables real-time job monitoring, evaluation, and instantaneous barrier validation.
